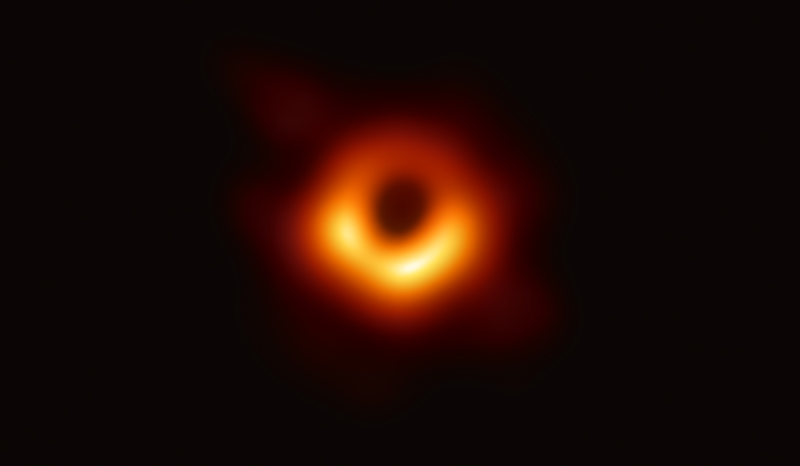
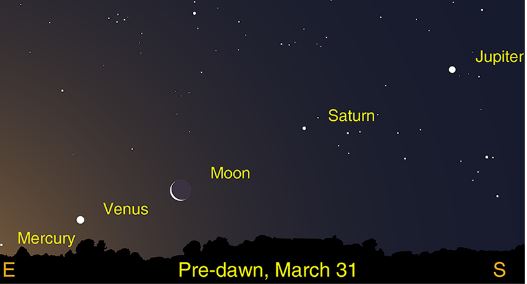
Scientists have obtained the first image of a black hole, using Event Horizon Telescope observations of the center of the galaxy M87. The image shows a bright ring formed as light bends in the intense gravity around a black hole that is 6.5 billion times more massive than the Sun. This long-sought image provides the strongest evidence to date for the existence of supermassive black holes and opens a new window onto the study of black holes, their event horizons, and gravity. Credit: Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration
An international collaboration presents paradigm-shifting observations of the gargantuan black hole at the heart of distant galaxy Messier 87
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) — a planet-scale array of eight ground-based radio telescopes forged through international collaboration — was designed to capture images of a black hole. Today, in coordinated press conferences across the globe, EHT researchers reveal that they have succeeded, unveiling the first direct visual evidence of a supermassive black hole and its shadow.
This breakthrough was announced today in a series of six papers published in a special issue of The Astrophysical Journal Letters. The image reveals the black hole at the center of Messier 87 [1], a massive galaxy in the nearby Virgo galaxy cluster. This black hole resides 55 million light-years from Earth and has a mass 6.5 billion times that of the Sun [2].
The EHT links telescopes around the globe to form an Earth-sized virtual telescope with unprecedented sensitivity and resolution [3]. The EHT is the result of years of international collaboration, and offers scientists a new way to study the most extreme objects in the Universe predicted by Einstein’s general relativity during the centennial year of the historic experiment that first confirmed the theory [4].
“We have taken the first picture of a black hole,” said EHT project director Sheperd S. Doeleman of the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian. “This is an extraordinary scientific feat accomplished by a team of more than 200 researchers.”
Black holes are extraordinary cosmic objects with enormous masses but extremely compact sizes. The presence of these objects affects their environment in extreme ways, warping spacetime and super-heating any surrounding material.