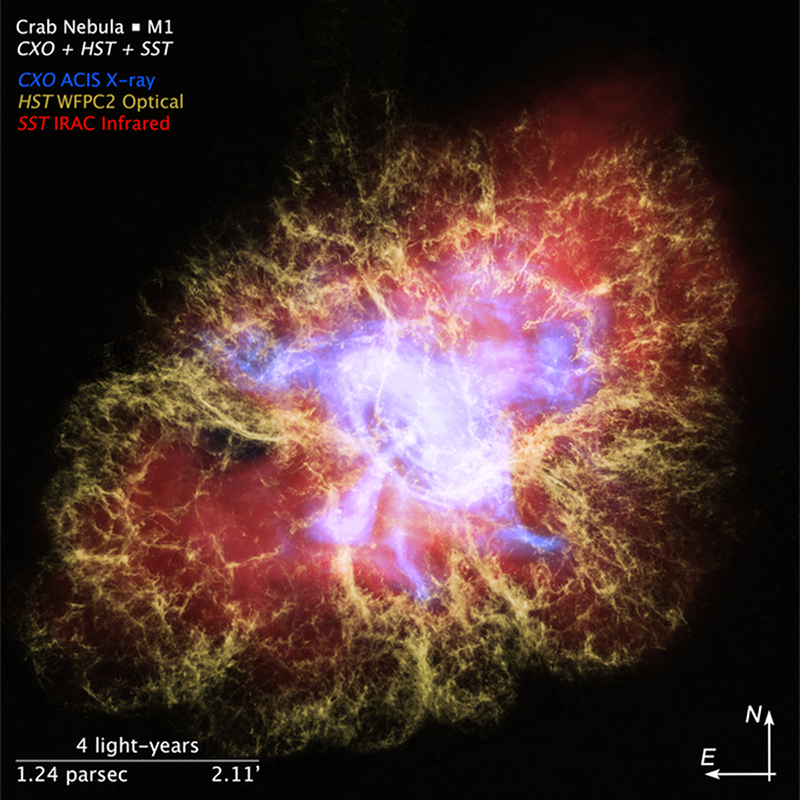
Image Credit: NASA
By: David Prosper
The Hubble Space Telescope celebrates its 30th birthday in orbit around Earth this month! It’s hard to believe how much this telescope has changed the face of astronomy in just three decades. It had a rough start — an 8-foot mirror just slightly out of focus in the most famous case of spherical aberration of all time. But subsequent repairs and upgrades by space shuttle astronauts made Hubble a symbol of the ingenuity of human spaceflight and one of the most important scientific instruments ever created. Beginning as a twinkle in the eye of the late Nancy Grace Roman, the Hubble Space Telescope’s work over the past thirty years changed the way we view the universe, and more is yet to come!
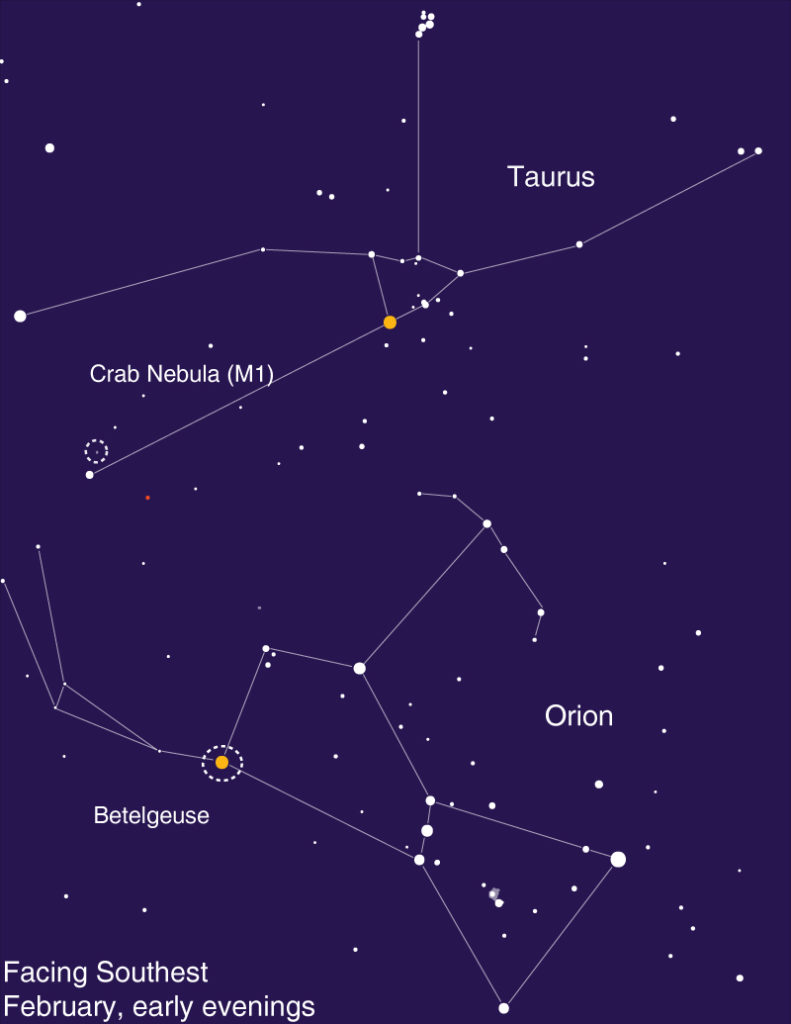
We’ve all seen the amazing images created by Hubble and its team of scientists, but have you seen Hubble yourself? You actually can! Hubble’s orbit – around 330 miles overhead — is close enough to Earth that you can see it at night. The best times are within an hour after sunset or before sunrise, when its solar panels are angled best to reflect the light of the Sun back down to Earth. You can’t see the structure of the telescope, but you can identify it as a bright star-like point, moving silently across the night sky. It’s not as bright as the Space Station, which is much larger and whose orbit is closer to Earth (about 220 miles), but it’s still very noticeable as a single steady dot of light, speeding across the sky. Hubble’s orbit brings it directly overhead for observers located near tropical latitudes; observers further north and south can see it closer to the horizon. You can find sighting opportunities using satellite tracking apps for your smartphone or tablet, and dedicated satellite tracking websites. These resources can also help you identify other satellites that you may see passing overhead during your stargazing sessions.
NASA has a dedicated site for Hubble’s 30th’s anniversary at bit.ly/NASAHubble30. The Night Sky Network’s “Why Do We Put Telescopes in Space?” activity can help you and your audiences discover why we launch telescopes into orbit, high above the interference of Earth’s atmosphere, at bit.ly/TelescopesInSpace. Amateur astronomers may especially enjoy Hubble’s images of the beautiful objects found in both the Caldwell and Messier catalogs, at bit.ly/HubbleCaldwell and bit.ly/HubbleMessier. As we celebrate Hubble’s legacy, we look forward to the future, as there is another telescope ramping up that promises to further revolutionize our understanding of the early universe: the James Webb Space Telescope!
Discover more about the history and future of Hubble and space telescopes at nasa.gov.

Hubble’s “first light” image. Even with the not-yet-corrected imperfections in its mirror, its images were generally sharper compared to photos taken by ground-based telescopes at the time. Image Credit: NASA