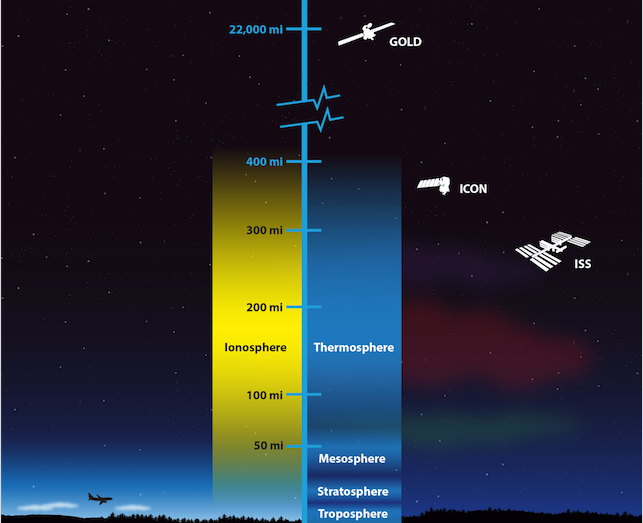
High above Earth is a very active part of our upper atmosphere called the ionosphere. The ionosphere gets its name from ions—tiny charged particles that blow around in this layer of the atmosphere.
How did all those ions get there? They were made by energy from the Sun!
Everything in the universe that takes up space is made up of matter, and matter is made of tiny particles called atoms. At the ionosphere, atoms from the Earth’s atmosphere meet up with energy from the Sun. This energy, called radiation, strips away parts of the atom. What’s left is a positively or negatively charged atom, called an ion.
The ionosphere is filled with ions. These particles move about in a giant wind. However, conditions in the ionosphere change all the time. Earth’s seasons and weather can cause changes in the ionosphere, as well as radiation and particles from the Sun—called space weather.
These changes in the ionosphere can cause problems for humans. For example, they can interfere with radio signals between Earth and satellites. This could make it difficult to use many of the tools we take for granted here on Earth, such as GPS. Radio signals also allow us to communicate with astronauts on board the International Space Station, which orbits Earth within the ionosphere. Learning more about this region of our atmosphere may help us improve forecasts about when these radio signals could be distorted and help keep humans safe.
In 2018, NASA has plans to launch two missions that will work together to study the ionosphere. NASA’s GOLD (Global-scale Observations of the Limb and Disk) mission launched in January 2018. GOLD will orbit 22,000 miles above Earth. From way up there, it will be able to create a map of the ionosphere over the Americas every half hour. It will measure the temperature and makeup of gases in the ionosphere. GOLD will also study bubbles of charged gas that are known to cause communication problems.
A second NASA mission, called ICON, short for Ionospheric Connection Explorer, will launch later in 2018. It will be placed in an orbit just 350 miles above Earth—through the ionosphere. This means it will have a close-up view of the upper atmosphere to pair with GOLD’s wider view. ICON will study the forces that shape this part of the upper atmosphere.
Both missions will study how the ionosphere is affected by Earth and space weather. Together, they will give us better observations of this part of our atmosphere than we have ever had before.
To learn more about the ionosphere, check out NASA Space Place: https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/ionosphere